AI security focuses on protecting artificial intelligence systems from cyber threats, data breaches, and malicious attacks.
1. Data Protection
AI systems depend on huge amounts of data.
If this data is stolen or exposed, it can lead to identity theft, privacy violations, or business harm.
AI security ensures data is encrypted, stored safely, and accessible only to authorized people.
2. Adversarial Attacks Prevention
Attackers can fool AI models by sending carefully designed, misleading inputs.
For example, changing small pixels in an image can trick AI into misidentifying objects.
AI security focuses on detecting and blocking these attacks so systems don’t make dangerous mistakes.
3. Model Robustness
AI needs to work correctly even when facing unexpected or noisy data.
Weak models can crash, give wrong answers, or behave unpredictably.
Security practices make models stronger, resilient, and more accurate under real-world conditions.
4. Access Control
AI systems often contain sensitive models, data, and business logic.
If hackers or unauthorized staff access them, they can steal data or modify functions.
Access control uses passwords, permissions, and authentication to protect systems from misuse.
5. Bias and Fairness Monitoring
AI can accidentally discriminate against groups if it’s trained with biased data.
This can cause unfair decisions in hiring, finance, healthcare, etc.
Security includes checking for bias, correcting errors, and ensuring fairness.
6. Explainability and Transparency
AI models are often “black boxes,” meaning people don’t know how they make decisions.
If we don’t understand AI behavior, mistakes or security issues may go unnoticed.
Explainability tools help humans interpret decisions, improve trust, and identify problems.
7. Secure Model Deployment
When AI is deployed into apps, websites, or devices, attackers may try to steal or copy it.
Secure deployment uses encryption, API protection, and safe storage to stop theft and tampering.
8. Continuous Monitoring
AI threats are constantly evolving.
Models must be monitored in real-time to detect unusual behavior, attacks, or performance drops.
Monitoring allows teams to react quickly and prevent damage.
9. Compliance & Regulations
AI systems must follow laws regarding privacy, data usage, and safety.
These include GDPR, AI Act, ethical guidelines, and industry standards.
Compliance reduces legal risk and ensures responsible AI development.
10. Incident Response and Recovery
No system is 100% safe.
When attacks happen, organizations need a plan to detect issues, fix vulnerabilities, and restore systems.
This prevents long-term damage and reduces downtime.
🔐 Why AI Security Matters
- Protects sensitive data
- Prevents manipulation and attacks
- Avoids harmful outcomes
- Ensures system reliability
- Builds trust among users
- Meets legal and ethical standards
- Protects critical systems
- Reduces long-term risk and cost
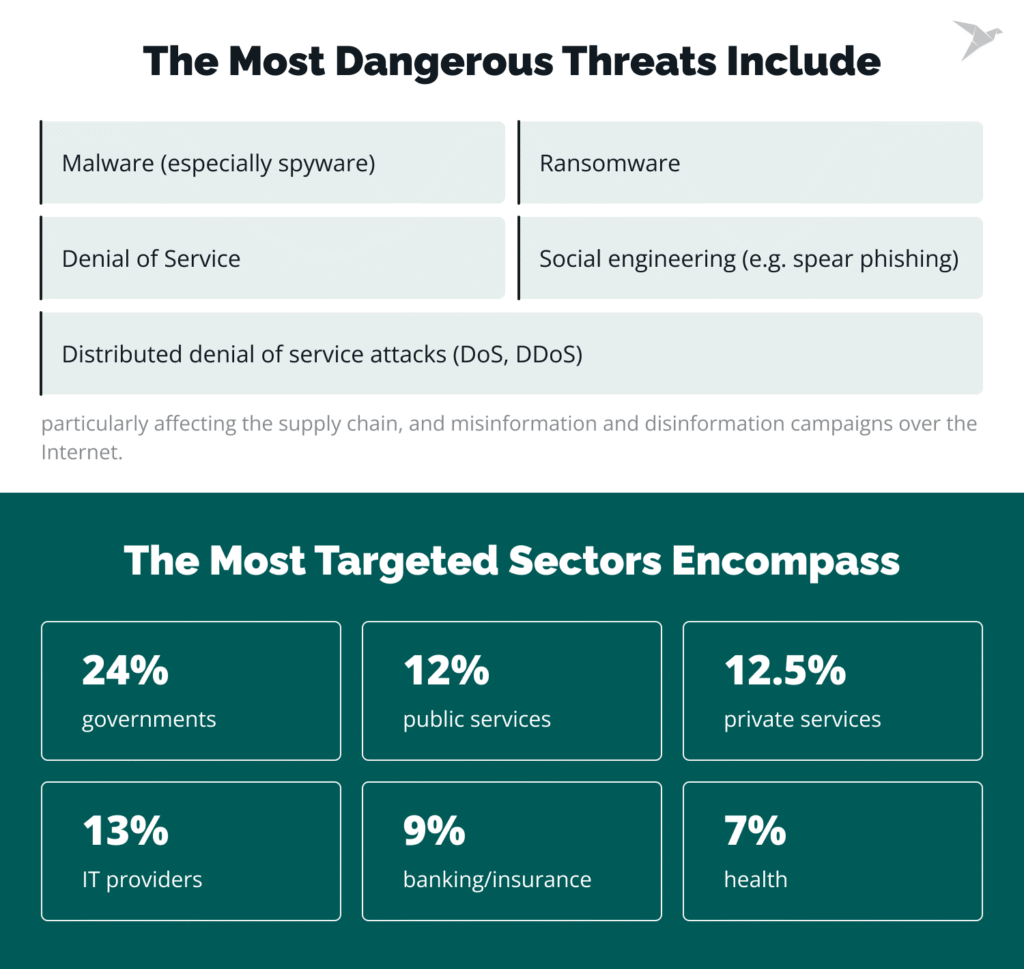
- The most dangerous threats include ransomware, malware, social engineering, denial of service, or distributed denial of service attacks (DoS, DDoS), particularly affecting the supply chain, and misinformation and disinformation campaigns over the Internet.
- The most targeted sectors encompass governments (24%), public services (12.5%), private services (12%), IT providers (13%), banking/insurance (9%), and health (7%).
- The threat of cybercrime has pushed malicious actors to exploit new tactics and technologies, lowering the entry barriers for cyberattacks. Cybercriminals now offer subscription services and starter kits, escalating the challenge of cybersecurity. The utilization of large language models like ChatGPT for writing malicious code further underscores the potential risks in the digital landscape. Additionally, AI security risks are becoming widespread as attackers use AI to automate and enhance their attack methods, making them more sophisticated and difficult to detect.





